Getting Started with randomforge
Friedrich Pahlke
2025-11-26
Source:vignettes/randomforge_getting_started.Rmd
randomforge_getting_started.RmdIntroduction
randomforge is an open-source R package providing a
transparent and modular framework for clinical trial
randomization.
This vignette gives a quick introduction on how to install the package,
create a simple project, configure a permuted block randomization
method, and generate subject allocations.
If you are new to randomization frameworks or want a minimal working example, this is a good place to start.
Installation
At this stage, randomforge is available only on
GitHub:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("RCONIS/randomforge")Creating a Randomization Project
Every workflow begins with a RandomProject stored inside
an in-memory RandomDataBase:
library(randomforge)
#> randomforge developer version 0.1.0.9046 loaded
# Create an in-memory randomization database
randomDataBase <- getRandomDataBase()
# Define a project
randomProject <- getRandomProject("Example Trial")
# Store the project in the database
randomDataBase$persist(randomProject)A project groups all configurations, subjects, and resulting allocations.
Defining a Randomization Configuration
A configuration defines:
- treatment arms
- allocation parameters
- random number buffer settings
- seeds
- optional stratification
Example:
config <- getRandomConfiguration(
randomProject = randomProject,
treatmentArmIds = c("A", "B"),
seed = createSeed(),
ravBufferMinimumSize = 1000L,
ravBufferMaximumSize = 10000L
)
config
#> random-project: Example Trial [2025-11-26] 33c8fb09-53bf-4828-ad50-67e639fb0e9f
#> uniqueId: 850ca5eb-50a0-4c46-aa64-cb827b199e63
#> creationDate: 2025-11-26
#> seed: 7384896
#> ravBufferMinimumSize: 1000
#> ravBufferMaximumSize: 10000
#> treatmentArmIds: 'A', 'B'
# Store the configuration
randomDataBase$persist(config)Creating a Block Randomization Method
randomforge currently supports permuted block
randomization (PBR) as a fully working implementation.
You can define variable block sizes:
# Define variable block sizes
blockSizes <- getBlockSizes(config$treatmentArmIds, c(4, 6))
# Define a block randomization method
blockSizeRandomizer <- getRandomBlockSizeRandomizer(blockSizes)
blockSizeRandomizer
#> RandomBlockSizeRandomizer(seed = 4629104, numberOfValues = 1000, currentIndex = 1)
randomMethodPBR <- getRandomMethodPBR(
blockSizes = blockSizes,
fixedBlockDesignEnabled = FALSE,
blockSizeRandomizer = blockSizeRandomizer
)Create a Random Allocation Value Service
# Create a random allocation value service
ravService <- getRandomAllocationValueService()
ravService$createNewRandomAllocationValues(config)
#> Create 9000 new random allocation values (seed = 7384896)Quality control of the random numbers used for randomization can be visualized by
ravService |>
plot(usedValuesOnly = FALSE)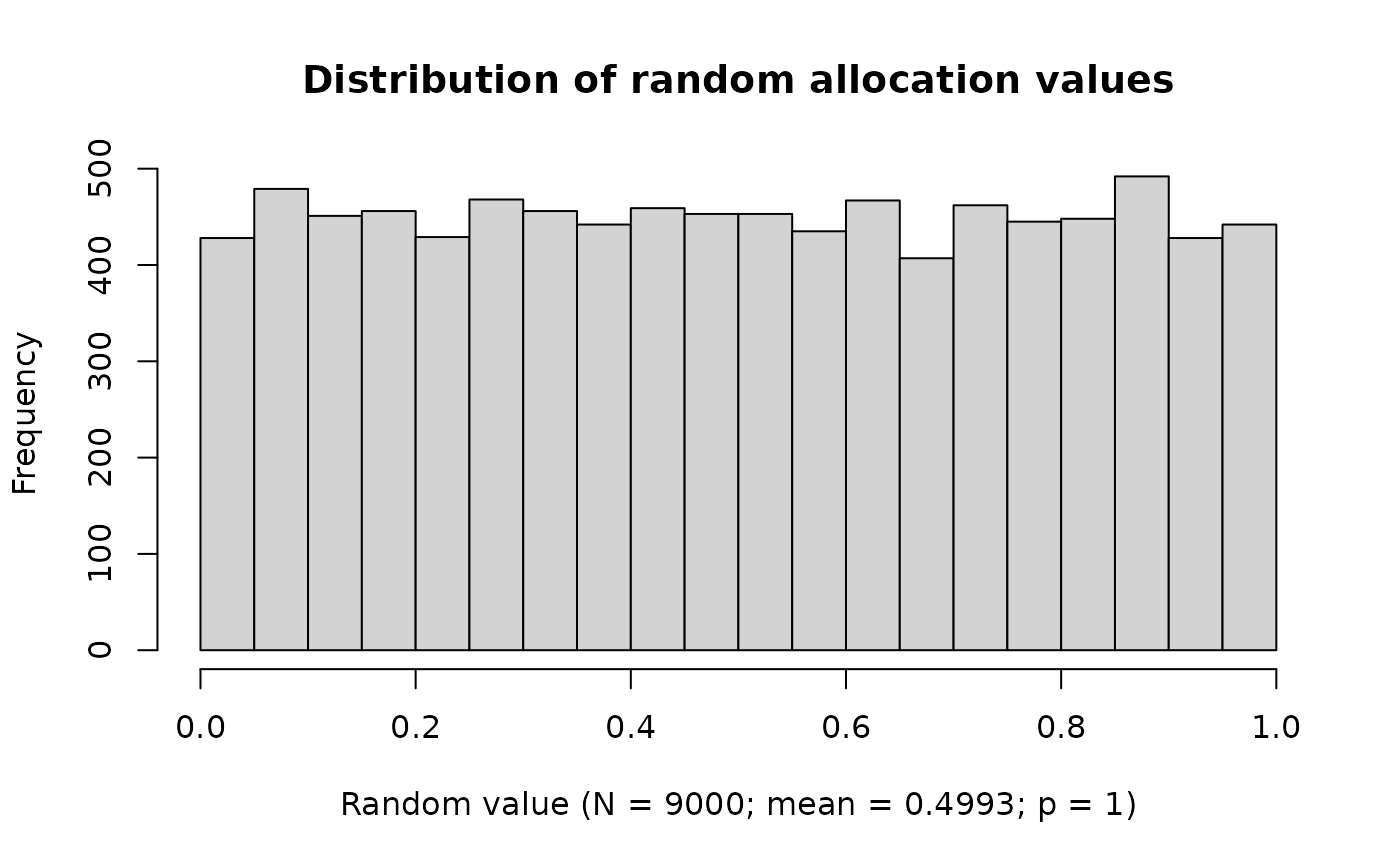
Other key performance indicators are planned for future releases.
Running Randomization
To generate assignments, create a random allocation value service,
then call getNextRandomResult().
# Create a few randomization results
resultList <- lapply(1:12, function(i) {
getNextRandomResult(
randomDataBase = randomDataBase,
randomProject = randomProject,
randomMethod = randomMethodPBR,
randomAllocationValueService = ravService
) |> suppressMessages()
})
ravService |>
plot()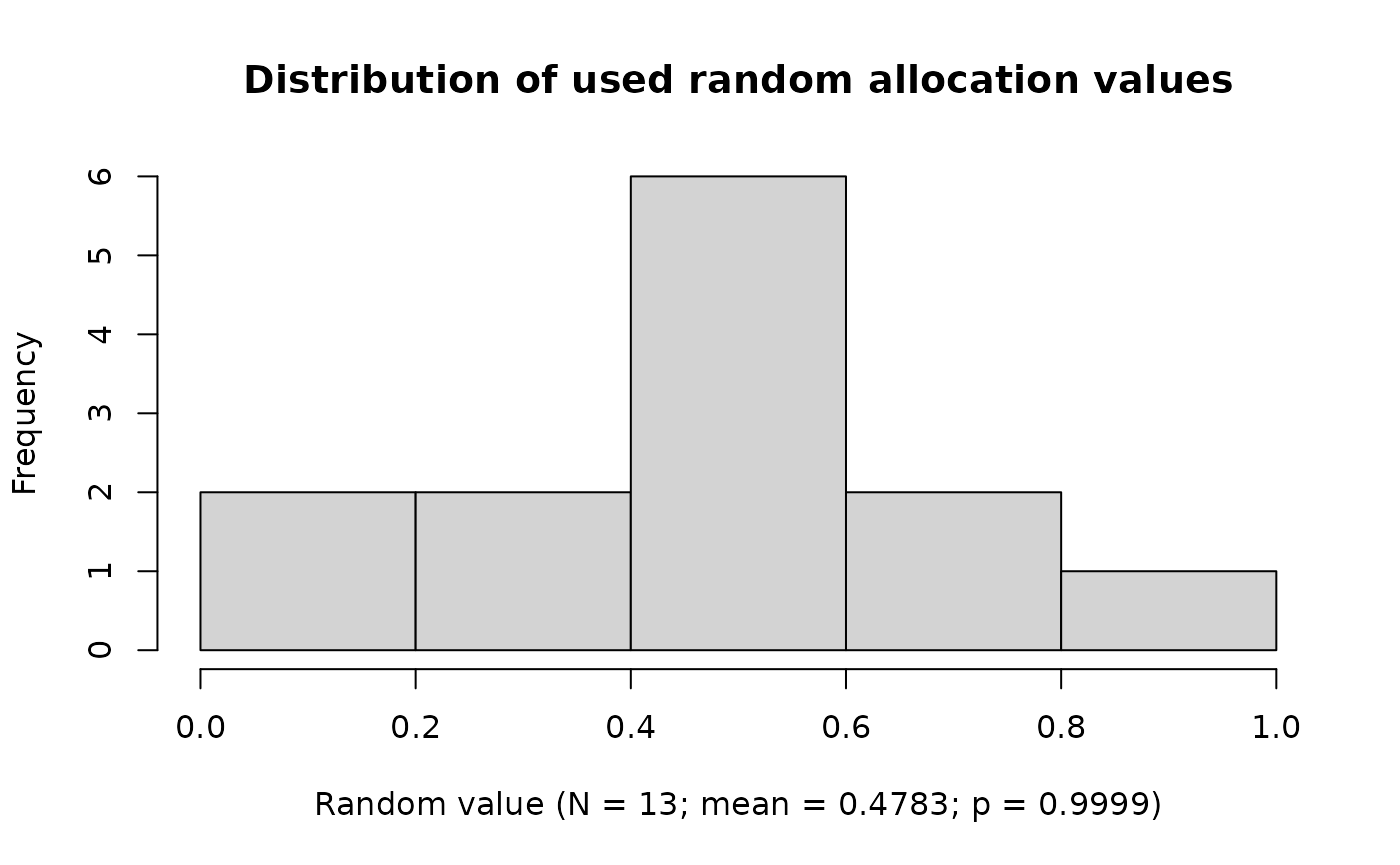
Inspecting the Results
All subjects and allocations stored in the database can be displayed as a data frame:
# Convert results to a data frame
resultData <- randomDataBase |>
as.data.frame()
resultData| project | random-number | treatment-arm | status | overall-levels-A | overall-levels-B | block-wise-levels-A | block-wise-levels-B | randomization-decision | unique-subject-id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Trial | 1 | A | RANDOMIZED | 1 | 0 | A:1/3 | B:0/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.0953753066714853] | 8626d10a-83f8-4723-bfc5-bb9d962778a6 |
| Example Trial | 2 | A | RANDOMIZED | 2 | 0 | A:2/3 | B:0/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.482989687006921] | 59d93e7c-eff3-4b4e-b105-f0b9358d9d8c |
| Example Trial | 3 | B | RANDOMIZED | 2 | 1 | A:2/3 | B:1/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.741397644625977] | 2296b7f9-edeb-44ef-867b-c2040a71c14b |
| Example Trial | 4 | B | RANDOMIZED | 2 | 2 | A:2/3 | B:2/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.939893207512796] | 8940e01d-dff8-4f1e-8eae-389c1399f7f9 |
| Example Trial | 5 | B | RANDOMIZED | 2 | 3 | A:2/3 | B:3/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.526956472313032] | 52c34a1b-aba8-4c43-8a4e-89ea39383301 |
| Example Trial | 6 | A | RANDOMIZED | 3 | 3 | A:3/3 | B:3/3 | range-set[A=[0,1], B=[1,1]; rav=0.312386621255428] | 5dfb3e4f-5739-4037-a0c6-284073f3fab7 |
| Example Trial | 7 | B | RANDOMIZED | 3 | 4 | A:0/3 | B:1/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.535009081242606] | e20c7127-0305-43ff-9480-5ac431b791af |
| Example Trial | 8 | B | RANDOMIZED | 3 | 5 | A:0/3 | B:2/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.600243803812191] | 8308ff81-9d46-4a88-bd32-b292211f39ff |
| Example Trial | 9 | B | RANDOMIZED | 3 | 6 | A:0/3 | B:3/3 | range-set[A=[0,0.5], B=[0.5,1]; rav=0.564123915275559] | dfabc7a6-0160-4c72-9b3b-edb2a076db89 |
| Example Trial | 10 | A | RANDOMIZED | 4 | 6 | A:1/3 | B:3/3 | range-set[A=[0,1], B=[1,1]; rav=0.443886212306097] | 8b7860ea-e446-43d0-a636-6c712d1eec5c |
| Example Trial | 11 | A | RANDOMIZED | 5 | 6 | A:2/3 | B:3/3 | range-set[A=[0,1], B=[1,1]; rav=0.10632219677791] | 53d9732e-be4e-4a73-976e-972f8bce2472 |
| Example Trial | 12 | A | RANDOMIZED | 6 | 6 | A:3/3 | B:3/3 | range-set[A=[0,1], B=[1,1]; rav=0.559311755700037] | b462981b-f3ce-4062-a89e-105d69963a78 |
Exporting to Excel (Optional)
randomforge supports exporting subject lists or
randomization results via writeExcelFile():
writeExcelFile(resultData, "randomization_list.xlsx")What’s Next?
The project is in an early phase, and many extensions are planned:
- covariate-adaptive methods (e.g., minimization)
- response-adaptive techniques
- stratified and center-based workflows
- audit trail and reporting components
- Shiny and API integration
To learn how to contribute, see the vignette: